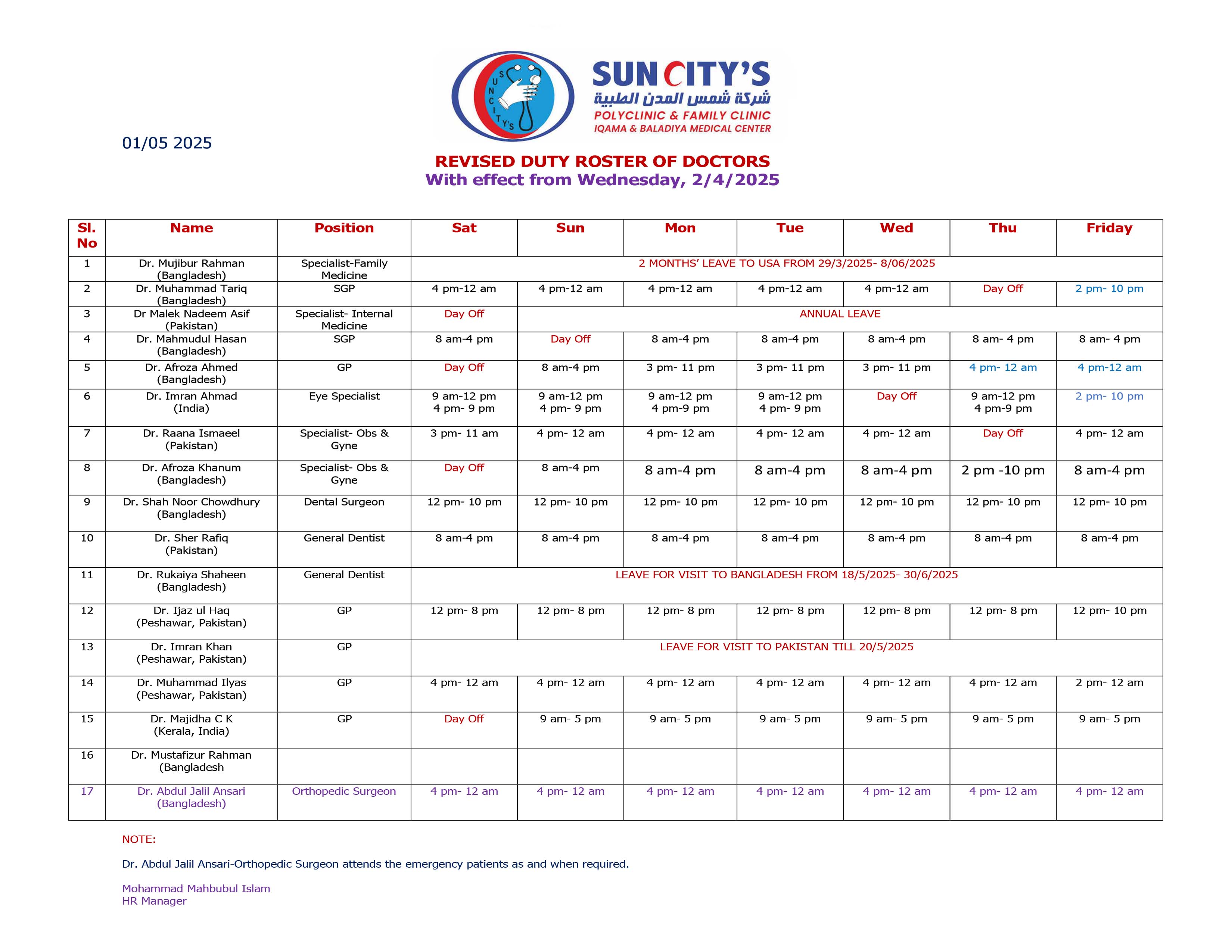
Duty Roster of Doctors
Role of a Physician in Medicine Physicians in this department are known as internists. They are experts in managing complex medical cases and chronic illnesses, providing comprehensive care to adults. Key Responsibilities: Patient Assessment: Conducting thorough history-taking and physical examinations. Diagnosis and Management: Identifying and treating a wide range of illnesses like diabetes, hypertension, and infections. Preventive Care: Promoting health through screenings, lifestyle modifications, and vaccination programs. Coordination of Care: Referring patients to specialists and collaborating with multidisciplinary teams for holistic care. Subspecialties in Internal Medicine The medicine department includes several subspecialties for advanced care: Cardiology: Focused on heart diseases (e.g., coronary artery disease, arrhythmias). Gastroenterology: Managing digestive system disorders (e.g., ulcers, liver disease). Pulmonology: Specializing in lung and respiratory conditions (e.g., asthma, COPD). Nephrology: Focused on kidney diseases and dialysis care. Endocrinology: Treating hormonal imbalances (e.g., diabetes, thyroid disorders). Rheumatology: Managing autoimmune and joint disorders (e.g., arthritis, lupus). Infectious Diseases: Specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of complex infections. Hematology/Oncology: Focusing on blood disorders and cancer management. Training Pathway Medical School: 5–6 years to earn an MBBS or equivalent degree. Residency in Internal Medicine: 3–4 years of intensive training. Fellowship (Optional): 1–3 years for subspecialty expertise. Licensure and Certification: Meeting the requirements of local medical boards or councils. Common Conditions Treated Chronic Diseases: Hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia. Infectious Diseases: Tuberculosis, pneumonia, sepsis. Acute Illnesses: Stroke, myocardial infarction, acute kidney injury. Preventive Care Needs: Cancer screenings, managing risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Key Skills for Internists Diagnostic Acumen: Ability to interpret clinical signs and diagnostic results accurately. Communication: Explaining complex conditions and treatment plans to patients. Critical Thinking: Managing patients with multiple, coexisting diseases. Collaboration: Working seamlessly with specialists and healthcare teams. Scope and Workplaces Hospitals: General wards, intensive care units, and emergency departments. Outpatient Clinics: Managing chronic diseases and preventive care. Research: Exploring new treatments and guidelines for disease management. Academic Roles: Teaching medical students and mentoring residents.
"Suncity Polyclinic: Confidence in healthcare in Riyadh, where patients receive dedicated care."